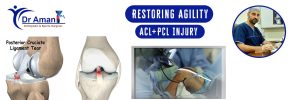
An ACL tear, also known as an Anterior Cruciate Ligament tear, is a common injury in orthopedics, particularly in sports-related activities or accidents involving the knee. The ACL is one of the four main ligaments in the knee, and it plays a crucial role in providing stability and support to the joint during movements like running, jumping, and pivoting.
When the ACL gets torn, it means that the ligament has been damaged or completely ruptured. This injury often occurs due to sudden and forceful movements, such as abruptly changing direction, landing awkwardly from a jump, or receiving a direct blow to the knee during sports like soccer, basketball, skiing, or football.
Symptoms of an ACL tear may include:
- Immediate and severe pain in the knee
- Swelling within the first few hours after the injury
- Instability or a feeling of the knee “giving way”
- A popping sound at the time of injury (sometimes heard or felt)
- Difficulty or inability to bear weight on the affected leg
- Limited range of motion in the knee
Diagnosis of an ACL tear is typically done through a physical examination by an orthopedic doctor, evaluation of the patient’s medical history, and the use of imaging tests, such as an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), to confirm the severity of the injury.
Treatment options for an ACL tear vary depending on the patient’s age, activity level, the extent of the tear, and the presence of any associated injuries. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Non-surgical treatment: Rest, physical therapy, and the use of knee braces to stabilize the joint.
- Surgical reconstruction: This involves reconstructing the torn ACL using tissue grafts, often from the patient’s own body (autografts) or from a donor (allografts). The surgery is typically performed arthroscopically, which is a minimally invasive procedure.
- Rehabilitation: Post-surgery or non-surgical treatment, physical therapy is crucial to regain strength, stability, and range of motion in the knee.
It’s essential to promptly seek medical attention if you suspect an ACL tear, as early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly impact the recovery process and long-term knee function. Rehabilitation and adherence to medical advice are critical in restoring the knee’s function and preventing further injuries.