MPFL Reconstruction
MPFL Reconstruction
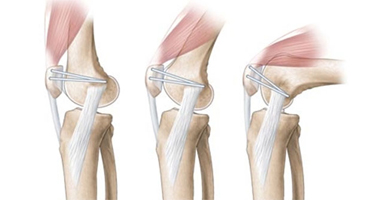
Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure indicated in patients with more severe patellar instability. The medial patellofemoral ligament is a band of tissue that extends from the femoral medial epicondyle to the superior aspect of the patella. The medial patellofemoral ligament is the major ligament that stabilizes the patella and helps in preventing patellar subluxation (partial dislocation) or dislocation. This ligament can rupture or get damaged when there is patellar lateral dislocation. Dislocation can be caused by a direct blow to the knee, twisting injury to the lower leg, strong muscle contraction, or because of congenital abnormality such as shallow or malformed joint surfaces.
Basic Principles Of Ligament Reconstruction
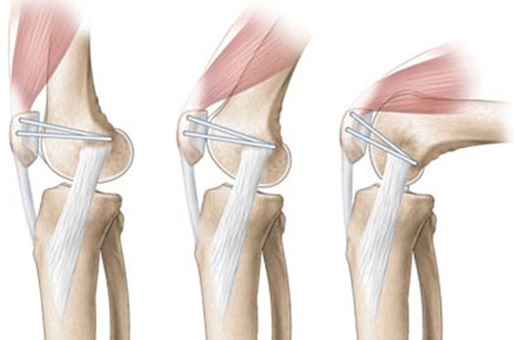
- Graft Selection: Strong and stiff graft
- Location: should be located isometrically
- Correct tension: should be appropriate
- Secure Fixation: Stable fixation
- Avoid condylar rubbing or impingement
Surgical Technique
The surgical procedure of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction involves the following steps:
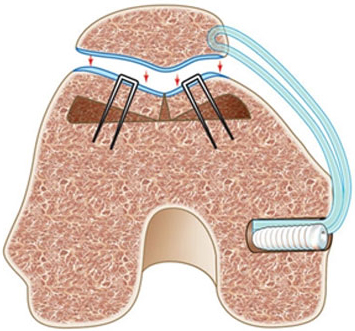
- Graft Selection and Harvest: Your surgeon may harvest some of your own tendons to reconstruct your ligament, or may use a cadaveric tendon (allograft). A 4 cm skin incision is made over your knee, at the medial aspect of the patella (knee cap), and a second usually smaller incision over the medial femoral condyle.
- Location of the femoral isometric point: The graft should be placed isometrically to prevent it from overstretching and causing failure during joint movements. The use of fluoroscopy during the case allows the surgeon to locate the correct isometric points for securing the graft.
- Correct tension: The tension is set in the graft with your knee flexed and the tension should be appropriate enough to control lateral excursion.
- Secure fixation: After bringing the tendon graft from the medial to the lateral side through the bone tunnel, it is turned onto the front surface of the patella where it is sutured.
- Avoid condylar rubbing and impingement: After graft fixation, the range of motion is checked to make sure there are no restrictions in patellar or knee movements. The graft should not impinge or rub against the medial femoral condyle. If it is detected, the graft is replaced in the proper position.
Post-Operative Care
A knee brace should be used during walking in the first 3-6 weeks after surgery. Avoid climbing stairs, squatting, and stretching your leg until there is adequate healing of the reconstruction.
Rehabilitation exercises, continuous passive motion, and active exercises will be recommended.

